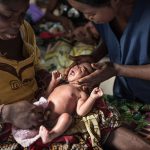
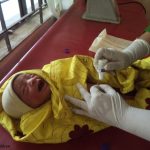
Ensuring optimal umbilical cord care at birth and during the first week of life is a crucial strategy to prevent life-threatening sepsis and cord infections and avert preventable neonatal deaths.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends clean, dry umbilical cord care for all newborns, including those born in facilities, at home, and in humanitarian settings. Proper cord care includes using clean, sterile blades and ties, keeping the stump clean using soap and water, and drying thoroughly with a clean cloth after getting wet. In most settings, proper clean, dry umbilical cord care is sufficient to prevent infection.
However, in settings where harmful traditional substances are placed on the cord, WHO recommends using chlorhexidine digluconate in addition to clean, dry cord care. Chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) is a broad-spectrum antiseptic that is available in a range of concentrations, and has been safely used for over 40 years for a variety of health-related applications. Its specific use for umbilical cord care was originally tested in three clinical trials in Nepal, Bangladesh, and Pakistan, in the form of 4% chlorhexidine, delivered through a 7.1% chlorhexidine digluconate gel. In 2013 the WHO added CHX to its Model List of Essential Medicines; and in 2014 the WHO issued guidelines on umbilical cord care, which included a formal recommendation on the use of chlorhexidine. This guidance was subsequently updated in 2022, reflecting the current recommendation for CHX use in certain settings.
CHX is the primary recommendation for settings where harmful traditional substances, such as oils, compresses, native plants, or other organic substances, are commonly placed on the umbilical cord. It was previously recommended for settings with high rates of home birth and neonatal mortality, where mothers, traditional birth attendants, and community health workers can be trained to administer CHX; as a result, this may be included as a recommendation in some national protocols.
In humanitarian settings, clean and dry umbilical cord care is the standard, but the use of chlorhexidine digluconate is also included as a recommendation in the Inter-Agency Field Manual for Reproductive Health in Humanitarian Settings (IAFM), the gold-standard for sexual and reproductive care in fragile and humanitarian settings. The IAFM includes CHX for cord care as a recommendation during the onset of emergencies, as part of the Minimum Initial Service Package (MISP), and as part of comprehensive maternal and newborn health (MNH) services. Additionally, chlorhexidine digluconate is included as a supplementary commodity in the Inter-Agency Reproductive Health Kits (RH Kits), which provide the supplies necessary to implement the MISP at the onset of a humanitarian response.
2.4m
newborn deaths worldwide in 2020
7
percent of deaths caused by sepsis and other infectious conditions of the newborn in 2020
All data on this page represents the most recent data available, unless otherwise noted. Please visit our Newborn Numbers page and download the Excel spreadsheet to explore the data further.
Key Resources
- Video on proper cord care for practitioners (2015)
- WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (22nd list, 2021)
- WHO Model List of Essential Medicines for Children (8th list, 2021)
- WHO recommendations on maternal and newborn care for a positive postnatal experience (2022)
- Inter-Agency Field Manual for Reproductive Health in Humanitarian Settings (2018)
- Minimum Initial Service Package (2018)
- Inter-Agency Reproductive Health Kits
- Chlorhexidine 7,1% digluconate (CHX) aqueous solution or gel (10ml): Reports of serious eye injury due to errors in administration (2020)
- Memorandum: Safety Concerns Over Misuse of Chlorhexidine (CHX) (2019)
- Alert No. 133: Chlorhexidine 7,1% digluconate (CHX): Reports of serious eye injury due to errors in administration (2019)